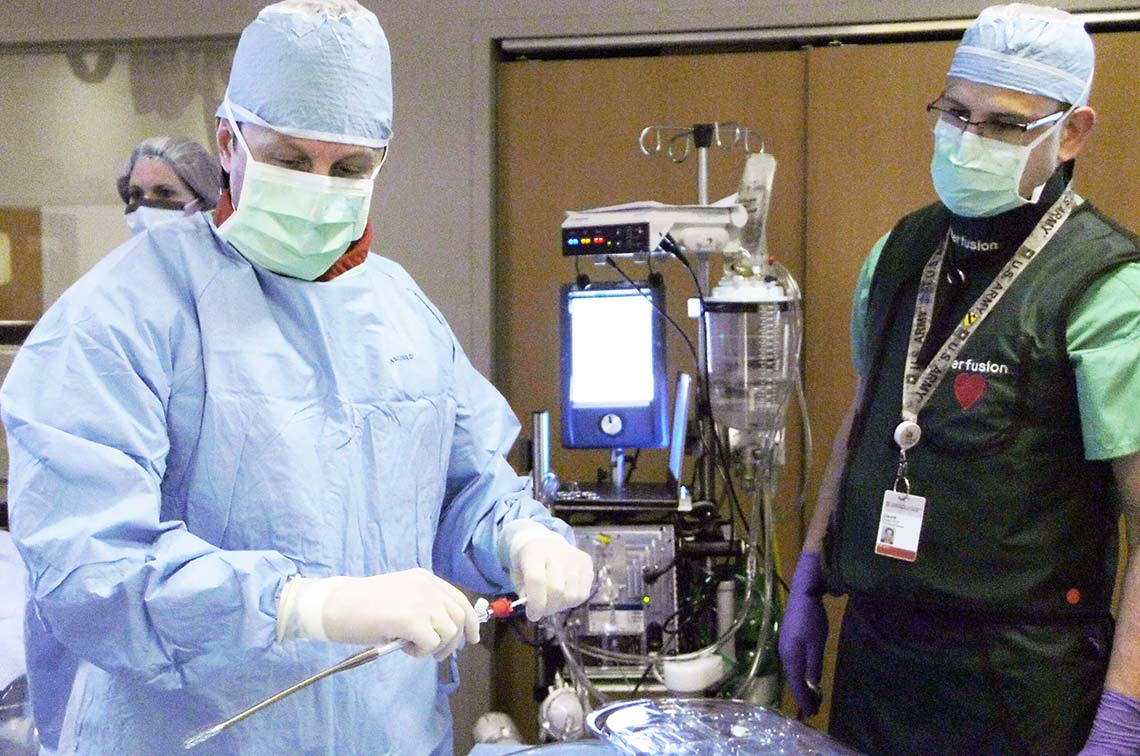
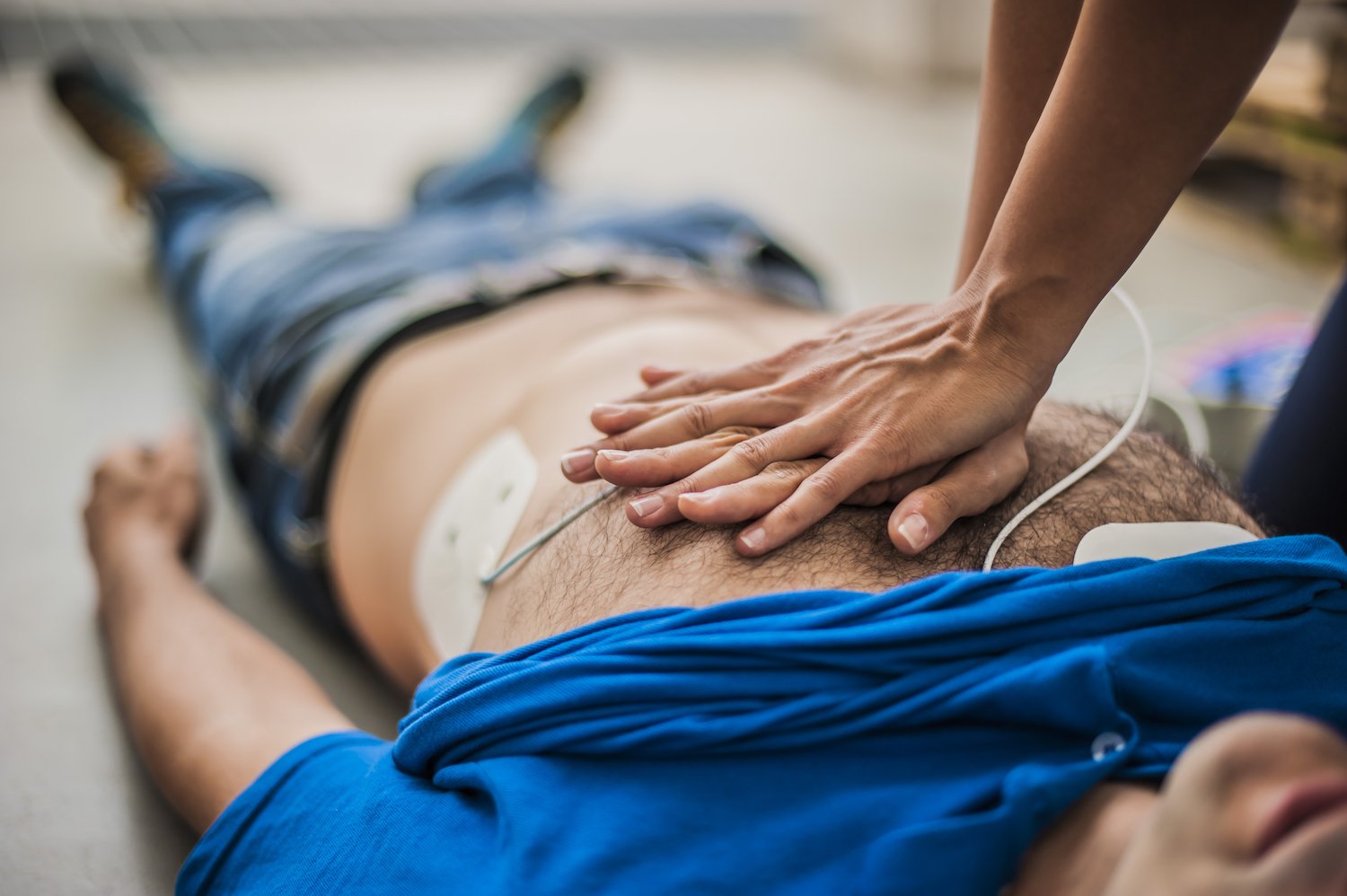
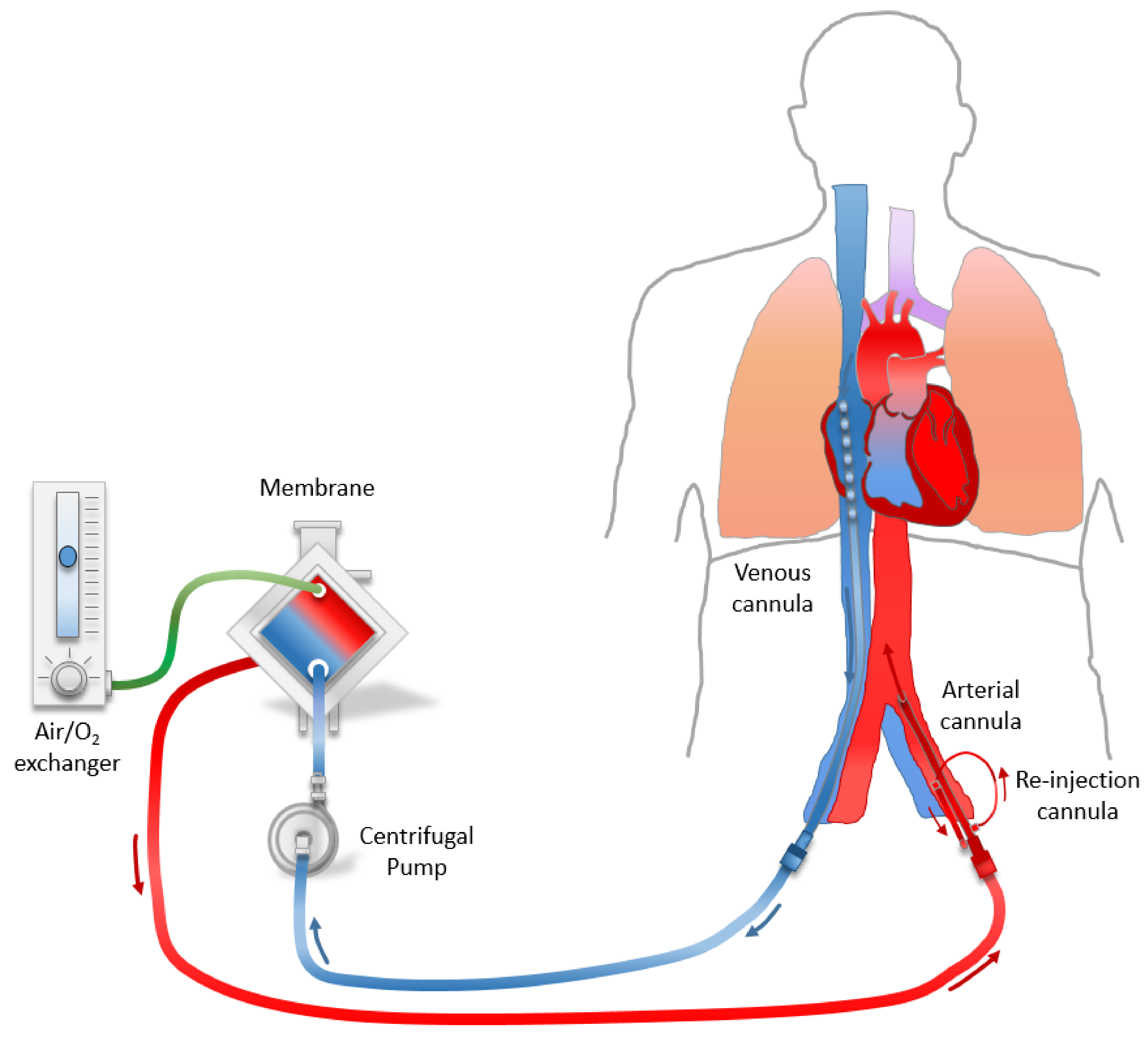
Ecpr In Cardiac Arrest - 19 until there are more robust data to the contrary, we recommend that the goal of ecpr is to establish adequate ecmo flow within 60 minutes of onset of cardiac arrest. Web in the setting of cardiac arrest, ecpr involves percutaneous cannulation of a femoral vein and artery, followed by the activation of the device, which subsequently maintains circulation until an appropriate recovery is made. Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased significantly in the past 10 years, in response to case reports and observational studies reporting encouraging results. Web in one center, ecpr survival after 90 minutes of ccpr was 14%.
Web in the setting of cardiac arrest, ecpr involves percutaneous cannulation of a femoral vein and artery, followed by the activation of the device, which subsequently maintains circulation until an appropriate recovery is made. Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased significantly in the past 10 years, in response to case reports and observational studies reporting encouraging results. 19 until there are more robust data to the contrary, we recommend that the goal of ecpr is to establish adequate ecmo flow within 60 minutes of onset of cardiac arrest. Web in one center, ecpr survival after 90 minutes of ccpr was 14%.
19 until there are more robust data to the contrary, we recommend that the goal of ecpr is to establish adequate ecmo flow within 60 minutes of onset of cardiac arrest. Web in one center, ecpr survival after 90 minutes of ccpr was 14%. Web in the setting of cardiac arrest, ecpr involves percutaneous cannulation of a femoral vein and artery, followed by the activation of the device, which subsequently maintains circulation until an appropriate recovery is made. Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased significantly in the past 10 years, in response to case reports and observational studies reporting encouraging results.
Cardiac Arrest ECPR Ohio State Wexner Medical Center
Web in one center, ecpr survival after 90 minutes of ccpr was 14%. Web in the setting of cardiac arrest, ecpr involves percutaneous cannulation of a femoral vein and artery, followed by the activation of the device, which subsequently maintains circulation until an appropriate recovery is made. Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of.
New ECPR Protocol Helps Some Cardiac Arrest Patients Survive 'Certain
Web in one center, ecpr survival after 90 minutes of ccpr was 14%. Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased significantly in the past 10 years, in response to case reports and observational studies reporting encouraging results. Web.
Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation for Out‐of‐Hospital
Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased significantly in the past 10 years, in response to case reports and observational studies reporting encouraging results. Web in one center, ecpr survival after 90 minutes of ccpr was 14%. Web.
Early ECPR for outofhospital cardiac arrest Best practice in 2018
Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased significantly in the past 10 years, in response to case reports and observational studies reporting encouraging results. Web in the setting of cardiac arrest, ecpr involves percutaneous cannulation of a femoral.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest 101 Symptoms, Causes & What To Do Homage
Web in the setting of cardiac arrest, ecpr involves percutaneous cannulation of a femoral vein and artery, followed by the activation of the device, which subsequently maintains circulation until an appropriate recovery is made. Web in one center, ecpr survival after 90 minutes of ccpr was 14%. 19 until there are more robust data to the contrary, we recommend that.
JCM Free FullText ECMO in Cardiac Arrest A Narrative Review of
Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased significantly in the past 10 years, in response to case reports and observational studies reporting encouraging results. 19 until there are more robust data to the contrary, we recommend that the.
Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation for Out‐of‐Hospital
19 until there are more robust data to the contrary, we recommend that the goal of ecpr is to establish adequate ecmo flow within 60 minutes of onset of cardiac arrest. Web in one center, ecpr survival after 90 minutes of ccpr was 14%. Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital.
eCPR and Cardiac Arrest
Web in the setting of cardiac arrest, ecpr involves percutaneous cannulation of a femoral vein and artery, followed by the activation of the device, which subsequently maintains circulation until an appropriate recovery is made. Web in one center, ecpr survival after 90 minutes of ccpr was 14%. 19 until there are more robust data to the contrary, we recommend that.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest What is it and what can you do about it? • MyHeart
19 until there are more robust data to the contrary, we recommend that the goal of ecpr is to establish adequate ecmo flow within 60 minutes of onset of cardiac arrest. Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased.
ECPR After Prolonged Cardiac Arrest Targeting Mechanisms of the No
Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased significantly in the past 10 years, in response to case reports and observational studies reporting encouraging results. Web in the setting of cardiac arrest, ecpr involves percutaneous cannulation of a femoral.
Web In One Center, Ecpr Survival After 90 Minutes Of Ccpr Was 14%.
Web the use of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (e‐ cpr) for the treatment of patients with out‐of‐hospital cardiac arrest who do not respond to conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation cpr) has increased significantly in the past 10 years, in response to case reports and observational studies reporting encouraging results. Web in the setting of cardiac arrest, ecpr involves percutaneous cannulation of a femoral vein and artery, followed by the activation of the device, which subsequently maintains circulation until an appropriate recovery is made. 19 until there are more robust data to the contrary, we recommend that the goal of ecpr is to establish adequate ecmo flow within 60 minutes of onset of cardiac arrest.