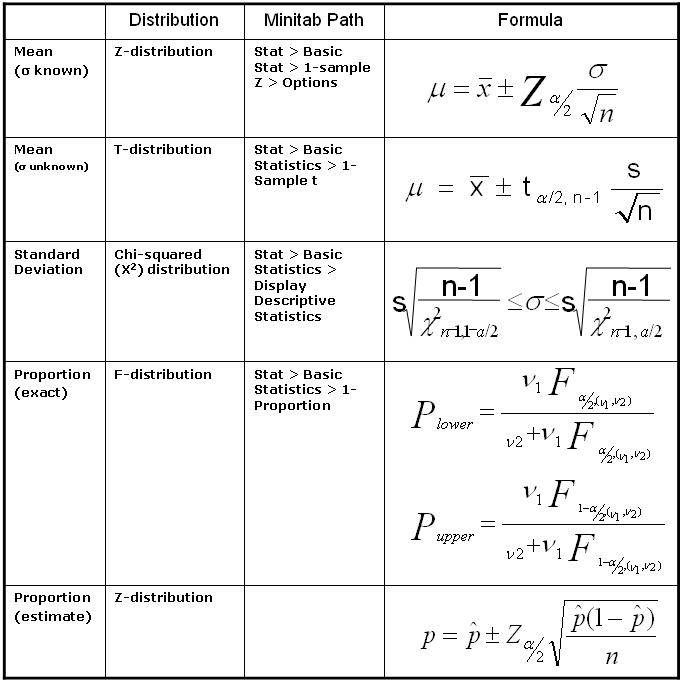
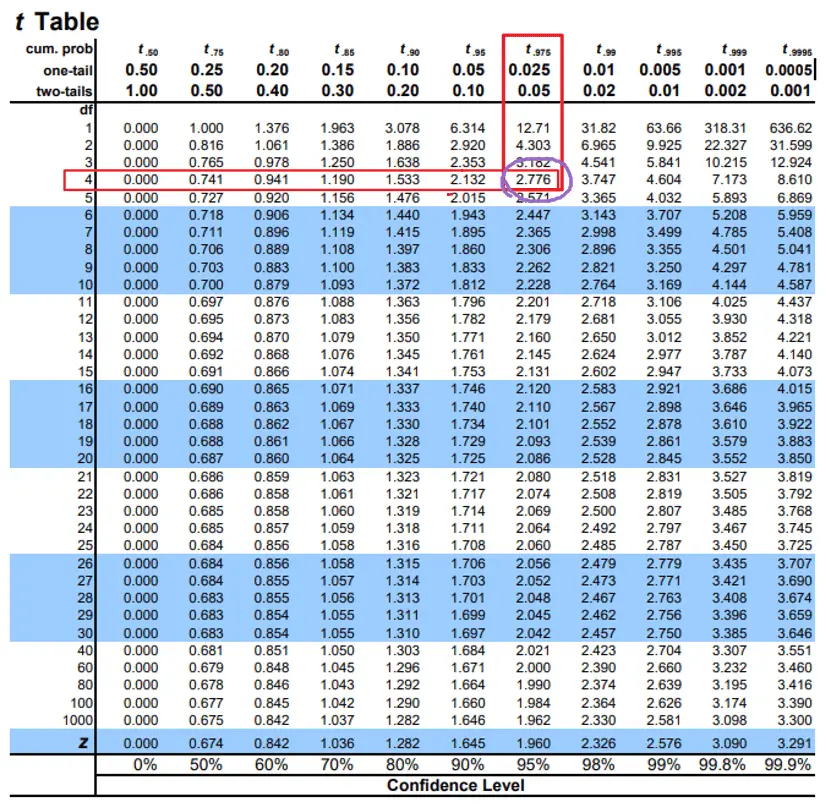
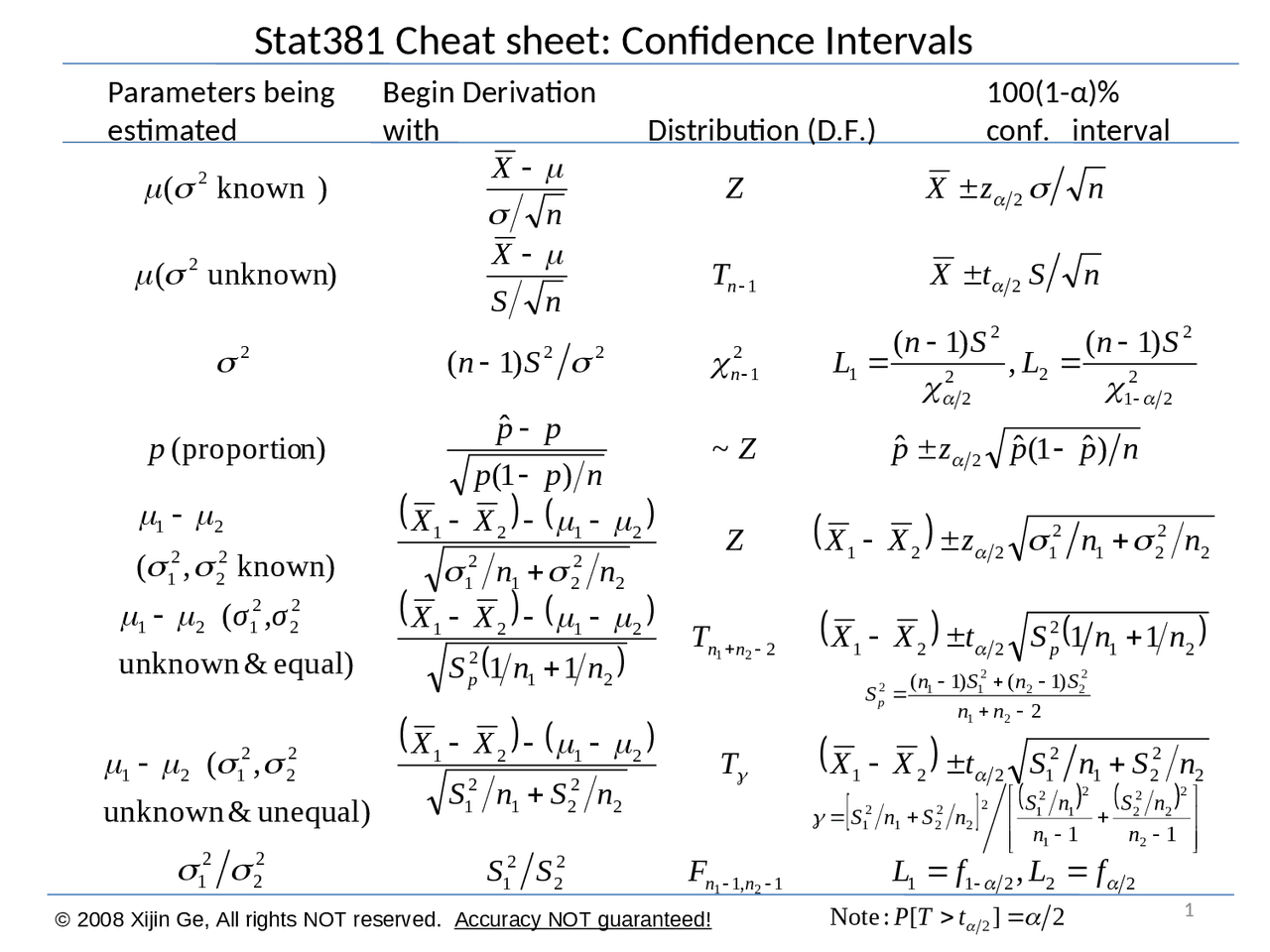
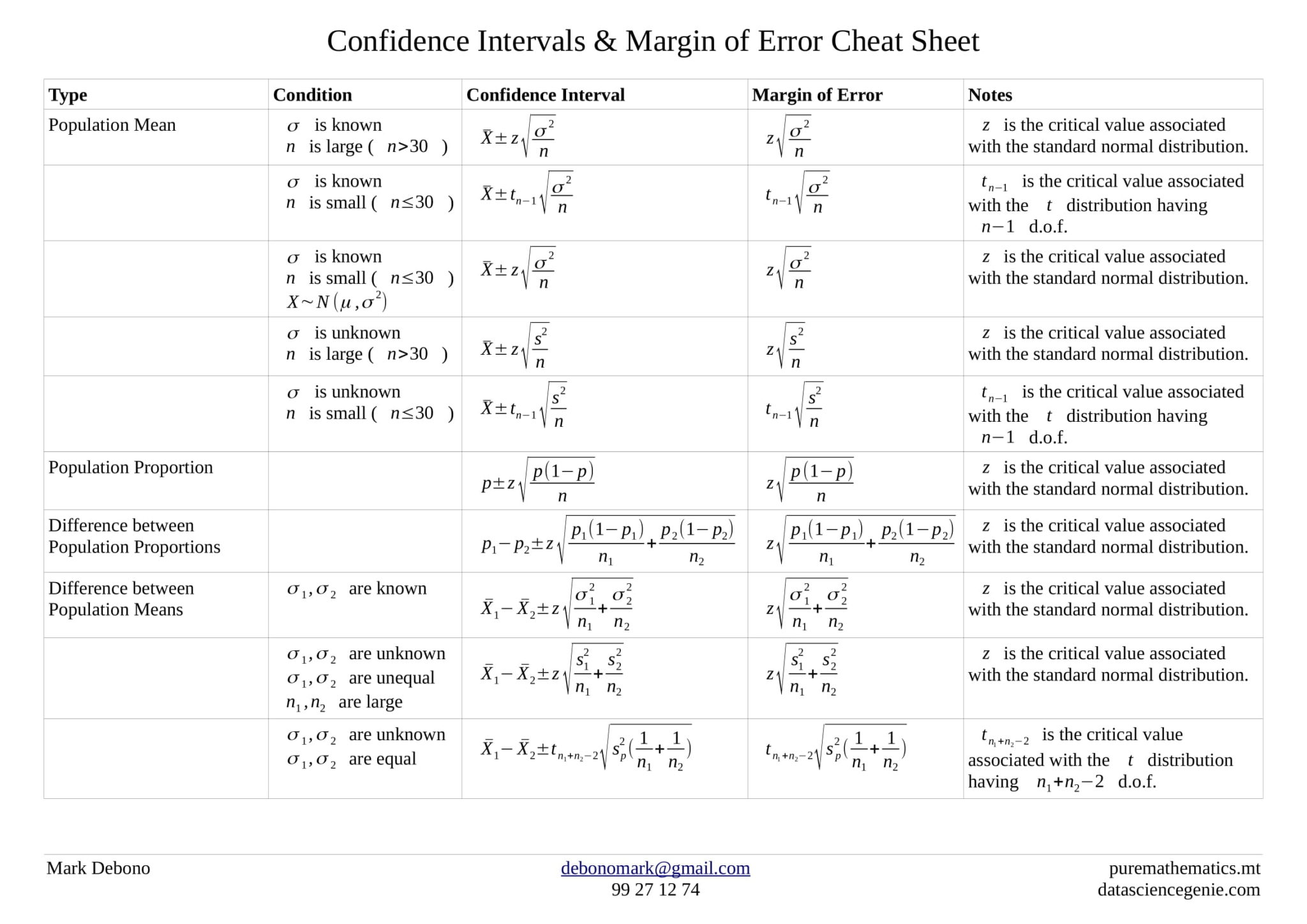
Confidence Interval Cheat Sheet - The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: A b means that a is less than or the same as b. Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. 1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2 2 12 2 22 1 11 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 12 2 12 confidence interval for and 11. = 1 hypothesis test with. Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. Web z interval t interval proportion interval 2 sample z interval symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 general • 2nd > vars • invnorm • stat > tests • 8: B means a is less than b. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; A > b means a is bigger than b.
The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. = 1 hypothesis test with. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; A b means that a is less than or the same as b. When do you use confidence intervals? 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. A > b means a is bigger than b. B means a is less than b.
A > b means a is bigger than b. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. = 1 hypothesis test with. B means a is less than b. Web z interval t interval proportion interval 2 sample z interval symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 general • 2nd > vars • invnorm • stat > tests • 8: 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: A b means that a is less than or the same as b. When do you use confidence intervals?
Confidence Interval Formulas Stupid Statistics Statistics math, Ap
The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: B means a is less than b. When do you use confidence intervals? 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a;
How to Calculate Confidence Interval 6 Steps (with Pictures) Math
The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. = 1 hypothesis test with. A > b means a is bigger than b.
How To Compute A 95 Confidence Interval / 95 Confidence Interval Chart
Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. = 1 hypothesis test with..
Confidence interval for two proportions calculator EmilieEmika
= 1 hypothesis test with. A > b means a is bigger than b. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. A b means that a is less than or the same as b.
Confidence Interval in Statistics Formula and Mathematical
A > b means a is bigger than b. Web z interval t interval proportion interval 2 sample z interval symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 general • 2nd > vars • invnorm • stat > tests • 8: The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how.
Cheat Sheet Confidence Intervals Principles of Statistics I STAT
{ the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; When do you use confidence intervals? A b means that a is less than or the same as b. 1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2.
Introductory Statistics Confidence Estimation
Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. = 1 hypothesis test with. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; A b means that.
Confidence Interval Cheat Sheet
1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2 2 12 2 22 1 11 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 12 2 12 confidence interval for and 11. Web confidence level = 1.
Confidence Intervals Cheat Sheet puremathematics.mt
1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2 2 12 2 22 1 11 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 12 2 12 confidence interval for and 11. The reasoning of statistical estimation.
A > B Means A Is Bigger Than B.
Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: 1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2 2 12 2 22 1 11 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 12 2 12 confidence interval for and 11. Web z interval t interval proportion interval 2 sample z interval symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 general • 2nd > vars • invnorm • stat > tests • 8:
{ The Point That Cuts The Interval (A+B) [A;
B means a is less than b. 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. = 1 hypothesis test with.
When Do You Use Confidence Intervals?
A b means that a is less than or the same as b.