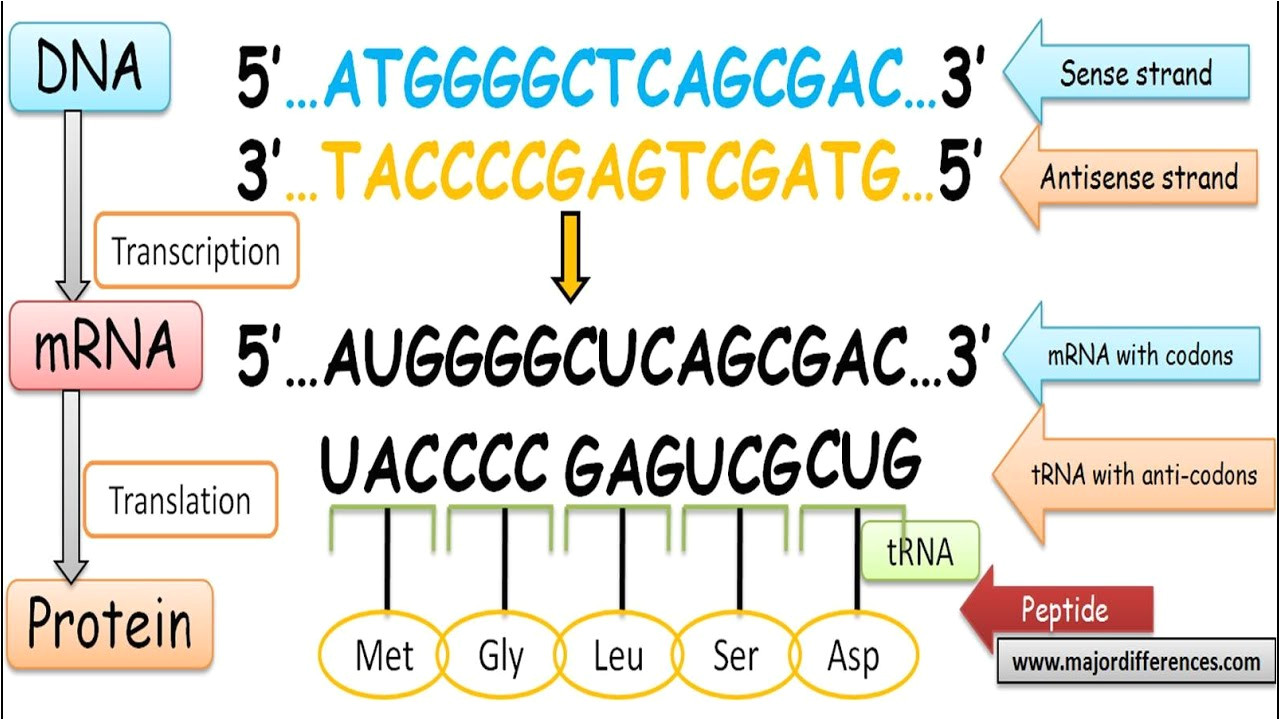
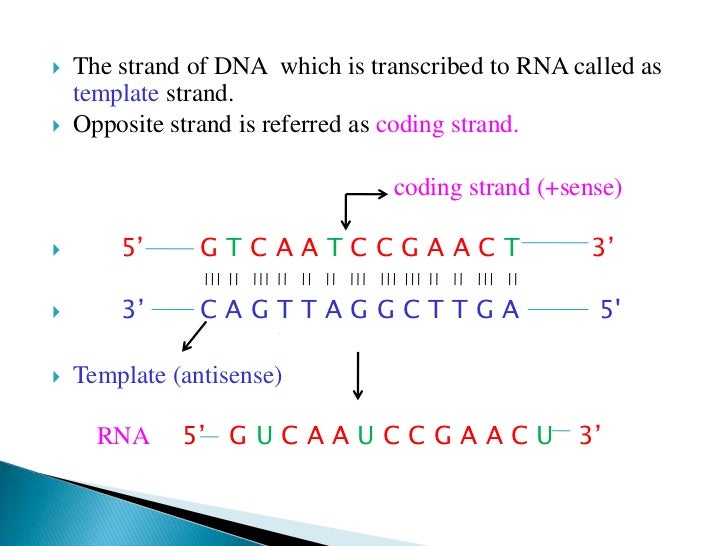
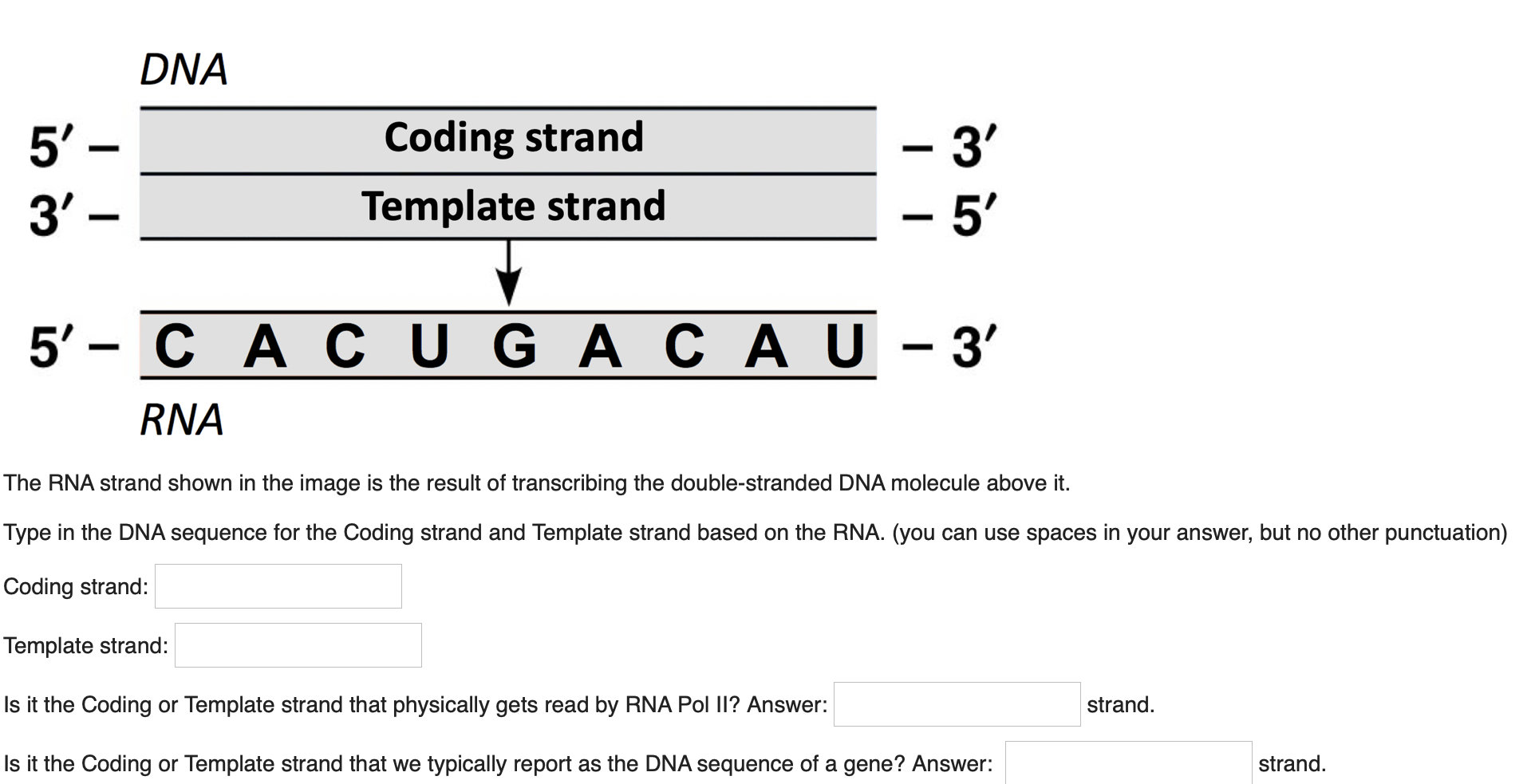
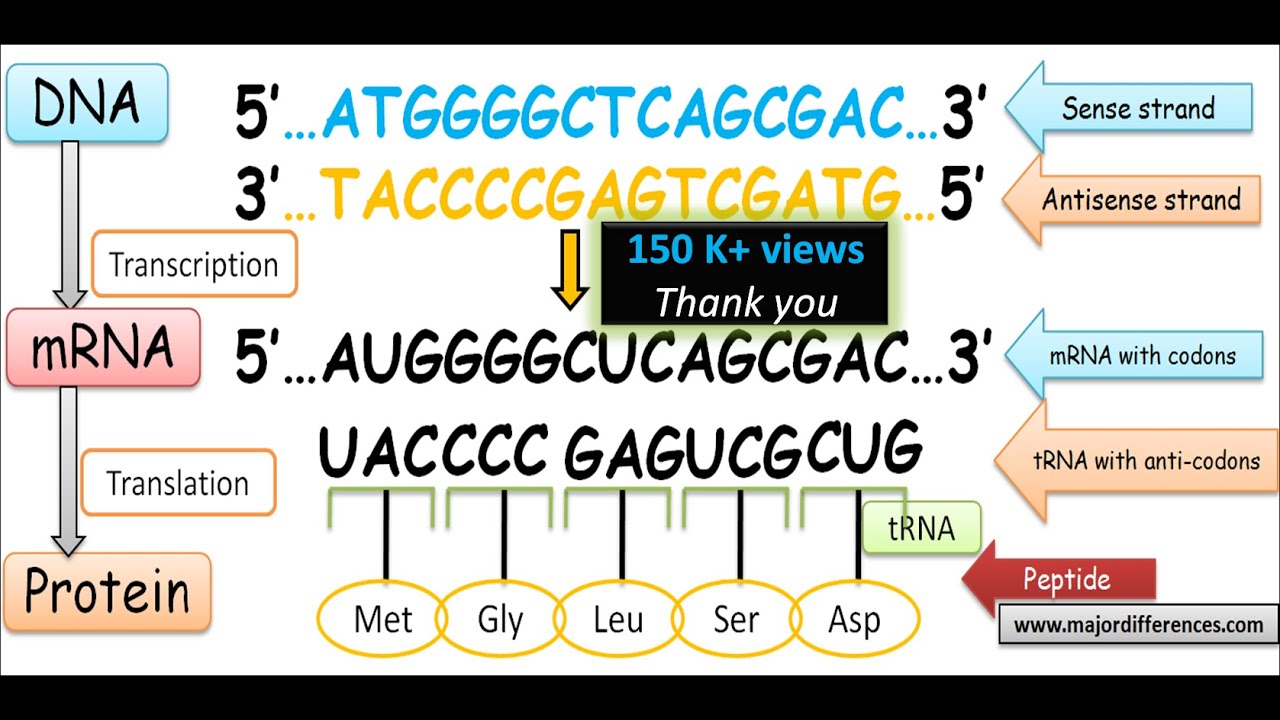
Coding Strand Template Strand - 5'tacaatgccagtggttcgcacatt 3' template strand 3' atgttacggtcaccaagcgtgtaa 5' coding strand. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. Rna polymerases begin transcription at dna sequences called promoters. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a. In summary, the coding strand contains the genetic information needed for protein. The four ribonucleotide triphosphates (rntps) are atp, gtp, utp, and ctp. Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna polymerases rna is synthesized from 5' to 3'. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Using the dna template strand provided and the mrna/amino acid chart you have been provided, indicate the strand of amino acids in the order they would be produced: The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a.
The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a. Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna polymerases rna is synthesized from 5' to 3'. 5'tacaatgccagtggttcgcacatt 3' template strand 3' atgttacggtcaccaagcgtgtaa 5' coding strand. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. Rna polymerases begin transcription at dna sequences called promoters. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up.
This strand is read by rna polymerase from 3′ to 5′. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a. Rna polymerases do not need primers to begin transcription. 5'tacaatgccagtggttcgcacatt 3' template strand 3' atgttacggtcaccaagcgtgtaa 5' coding strand. In summary, the coding strand contains the genetic information needed for protein. Rna polymerases begin transcription at dna sequences called promoters. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna polymerases rna is synthesized from 5' to 3'. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule.
Template vs. Nontemplate (Noncoding vs. Coding strand of DNA) YouTube
Rna polymerases do not need primers to begin transcription. This strand is read by rna polymerase from 3′ to 5′. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. 5'tacaatgccagtggttcgcacatt 3' template strand 3' atgttacggtcaccaagcgtgtaa 5' coding strand. This template strand is.
Coding Strand of DNA bartleby
The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t).
Classifications of transcriptional strand bias. a RNA polymerase uses
This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. This strand is read by rna polymerase from 3′ to 5′. Rna polymerases begin transcription at dna sequences called.
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand williamsonga.us
Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna polymerases rna is synthesized from 5' to 3'. This strand is read by rna polymerase from 3′ to 5′. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a. Write the similarities between the template and coding strand. The four ribonucleotide.
Transcription
Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. 5'tacaatgccagtggttcgcacatt 3' template strand 3' atgttacggtcaccaagcgtgtaa 5' coding strand. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a. Web.
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand
Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. In summary, the coding strand contains the genetic information needed for protein. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Rna polymerases begin transcription at dna sequences called promoters.
Solved DNA 5' 3' Coding strand Template strand 3' 5'
The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Rna polymerases do not need primers to begin transcription. Write the similarities between the template and coding strand. Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna polymerases rna is synthesized from 5' to 3'. The four ribonucleotide triphosphates (rntps) are atp, gtp, utp,.
IMP Coding (Sense) vs Template (AntiSense) Strands Biology activity
The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna polymerases rna is synthesized from 5' to 3'. 5'tacaatgccagtggttcgcacatt 3' template strand 3' atgttacggtcaccaagcgtgtaa 5' coding strand. Using.
Difference between Sense Strand and Antisense Strand of DNA YouTube
This strand is read by rna polymerase from 3′ to 5′. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. 5'tacaatgccagtggttcgcacatt 3' template strand 3' atgttacggtcaccaagcgtgtaa 5' coding strand. In summary, the coding strand contains the genetic information needed for protein.
The coding strand of DNA is 5'AATTCAAATTAGG3'
Using the dna template strand provided and the mrna/amino acid chart you have been provided, indicate the strand of amino acids in the order they would be produced: Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Rna polymerases begin transcription at dna sequences called promoters. 5'tacaatgccagtggttcgcacatt 3' template strand 3' atgttacggtcaccaagcgtgtaa 5' coding strand. In summary, the coding strand.
The Coding Strand Determines The Correct Nucleotide Sequence Of Mrna.
One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Rna polymerases begin transcription at dna sequences called promoters. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. 5'tacaatgccagtggttcgcacatt 3' template strand 3' atgttacggtcaccaagcgtgtaa 5' coding strand.
The Nontemplate Strand Is Referred To As The Coding Strand Because Its Sequence Will Be The Same As That Of The New Rna Molecule.
Write the similarities between the template and coding strand. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a. Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna polymerases rna is synthesized from 5' to 3'. This strand is read by rna polymerase from 3′ to 5′.
The Copy Of The Template Strand Is Read By Ribosomes, Which Then Produce A.
Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Using the dna template strand provided and the mrna/amino acid chart you have been provided, indicate the strand of amino acids in the order they would be produced: The four ribonucleotide triphosphates (rntps) are atp, gtp, utp, and ctp.
Rna Polymerases Do Not Need Primers To Begin Transcription.
In summary, the coding strand contains the genetic information needed for protein.