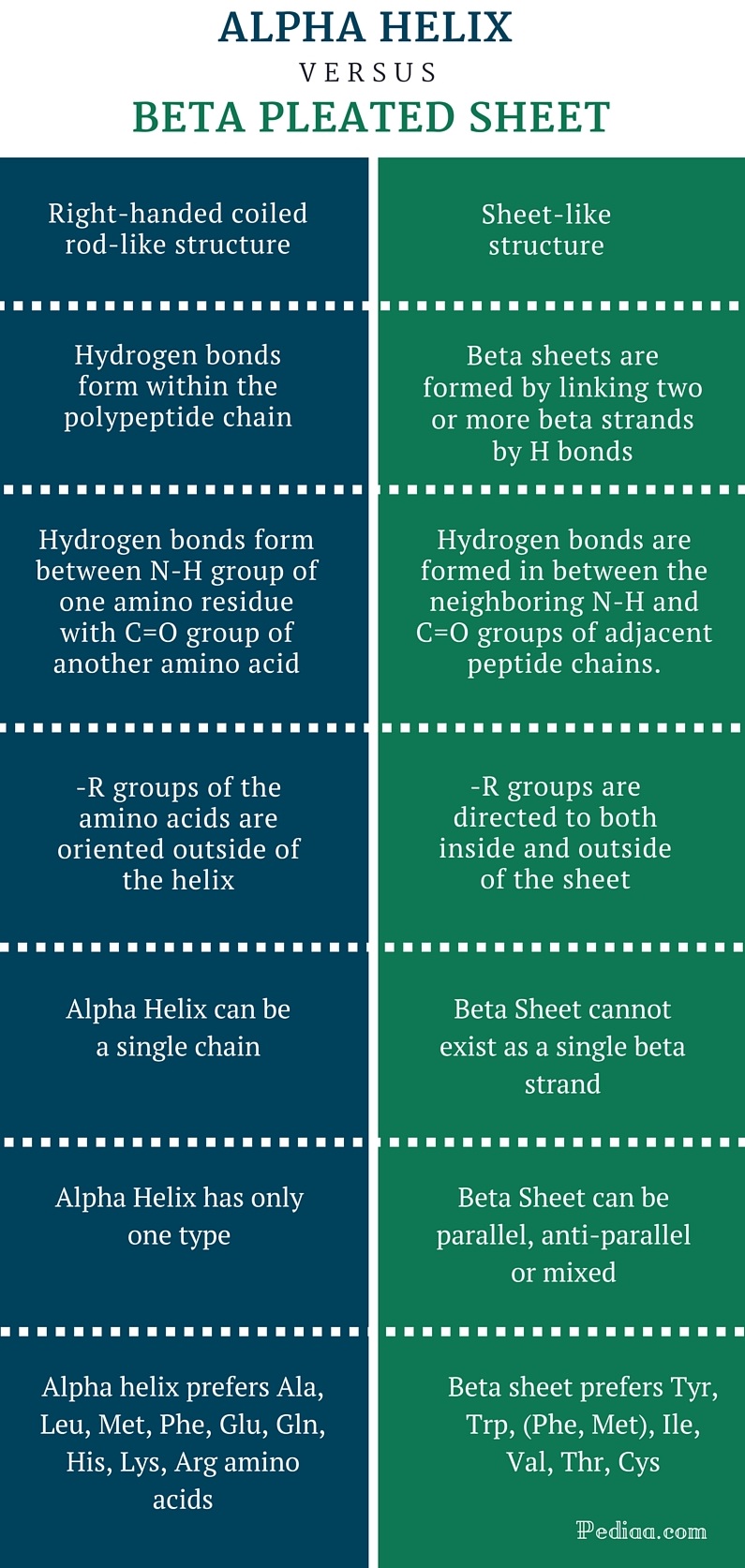
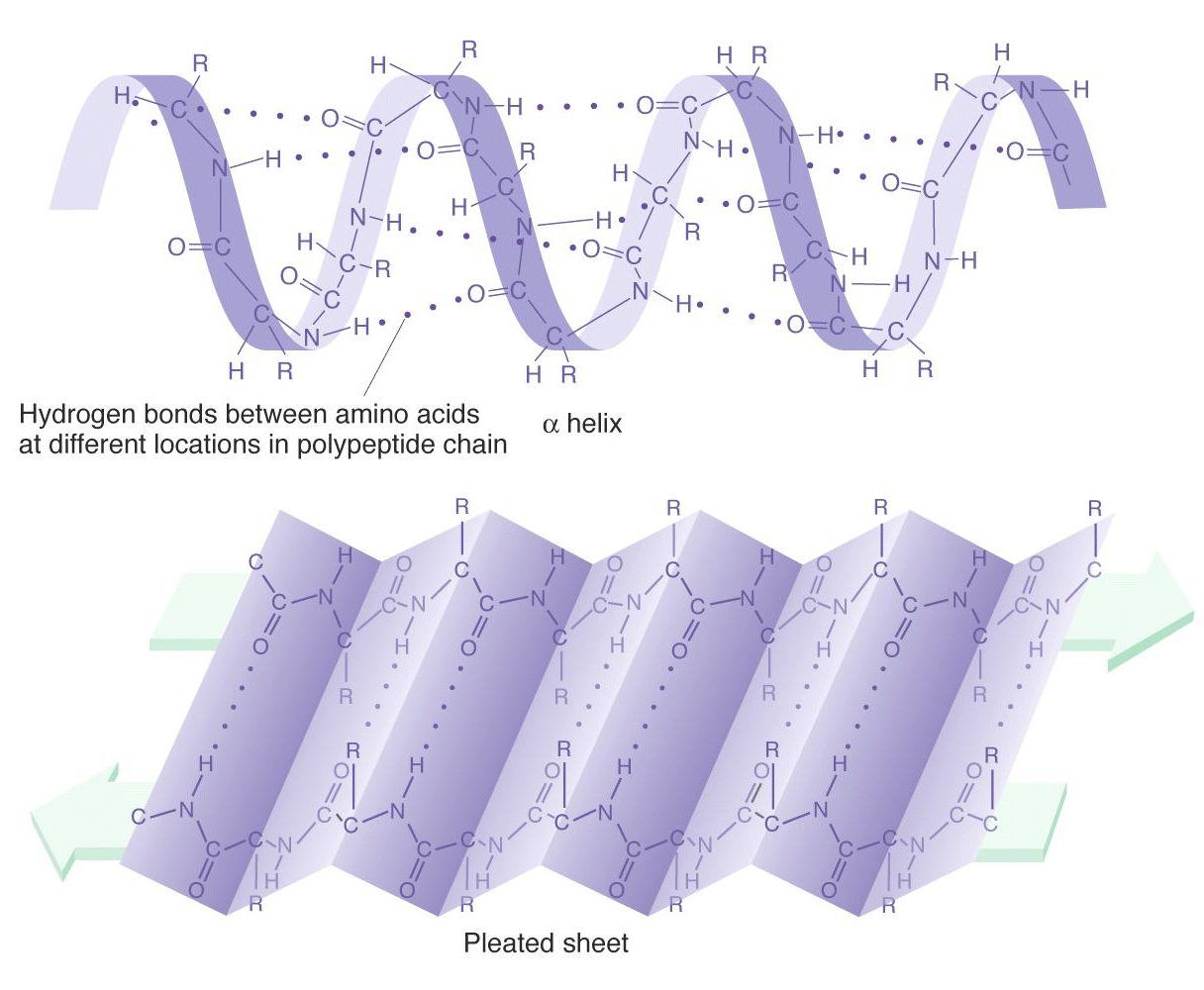
Alpha Helix Vs Beta Pleated Sheet - Web difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet shape. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. A helix with 2 residues/turn. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha.
Web difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet shape. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. A helix with 2 residues/turn. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the.
A helix with 2 residues/turn. Web difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet shape. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet
A helix with 2 residues/turn. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha..
Difference between Alpha Helix and Beta Helix
Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. A helix with 2 residues/turn. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. They both are.
Secondary structures of keratin protein (beta pleated sheets and alpha
The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. Web.
Alpha Helix vs Beta Pleated Sheet Diffzi
The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. Web difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet shape. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. A helix with 2 residues/turn. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet
Web difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet shape. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between.
Disulfide bonds Biochemistry3rst
Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. Web difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet shape. A helix with 2 residues/turn. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet
Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are held in.
MGA2_0325
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. Web difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet shape. The other portions of the polymer backbone that.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet Compare the
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. A.
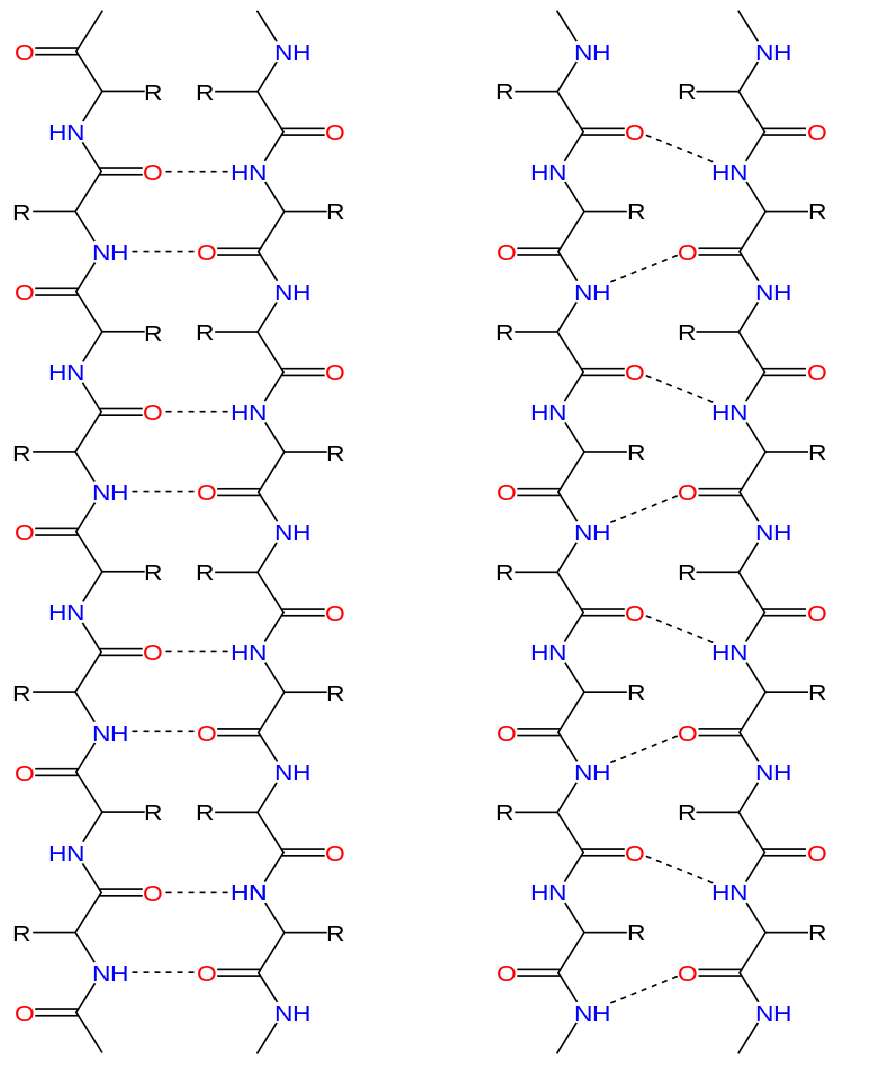
[Solved] How many hydrogen bonds involving the backbone CO and NH can
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. Web difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet shape. The other portions of the polymer backbone that.
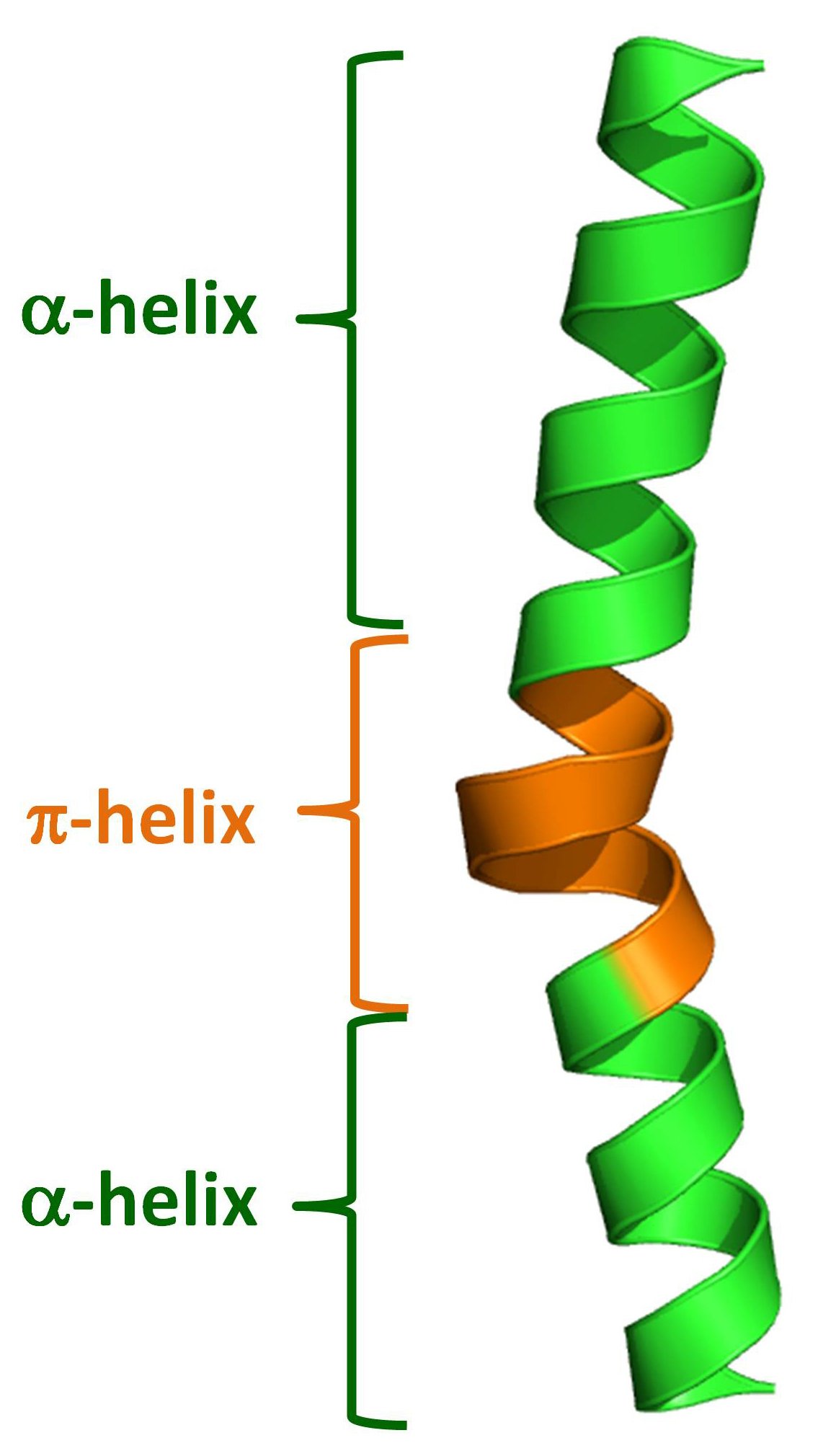
Web The Most Common Types Of Secondary Structures Are The Α Helix And The Β Pleated Sheet.
The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. A helix with 2 residues/turn. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. Web difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet shape.
They Both Are Shaped By Hydrogen Bonding Between The Carbonyl O Of One Amino Acid And The Amino H Of Another.
The arrangement of each successive peptide plane is pleated due to the tetrahedral nature of the alpha.





![[Solved] How many hydrogen bonds involving the backbone CO and NH can](https://cdn.testbook.com/images/production/quesImages/qImage646f23abed4806260c7a04d2.png)