Airflow Jinja Template - You can use jinja templating with every parameter that is marked as “templated” in the documentation. Assuming you have conn id test_conn you can use macros directly via: One for each of the jinja template variables and a templates_dict argument. Web 2 answers sorted by: Web 2 answers sorted by: 5 it works but i'm being asked to not use the variable module and use jinja templating instead this is not accurate recommendation and i'll explain why. S3_bucket = variable.get ('bucket_name') print (s3_bucket) example_task () How to apply jinja templates in your code. 2 to add to sergiy's response, it depends on where you want to make your intervention. Web templates reference¶ variables, macros and filters can be used in templates (see the jinja templating section) the following come for free out of the box with airflow.
It makes sense that specific parameters in the airflow world (such as certain parameters to pythonoperator ) get templated by. Which operator fields can be templated and which cannot. You can use jinja templating with every parameter that is marked as “templated” in the documentation. Web templates reference¶ variables, macros and filters can be used in templates (see the jinja templating section) the following come for free out of the box with airflow. One for each of the jinja template variables and a templates_dict argument. Sergiy's is the only way for it to work with your template: There is absolutely no problem with doing: { { conn.test_conn.host }}, { { conn.test_conn.login }}, { { conn.test_conn.password }} and so on. Web airflow leverages jinja, a python templating framework, as its templating engine. Web 2 answers sorted by:
How to apply jinja templates in your code. There is absolutely no problem with doing: Sergiy's is the only way for it to work with your template: 2 to add to sergiy's response, it depends on where you want to make your intervention. { { params.etl_date if params.etl_date is not none else execution_date.strftime ('%y%m%d') }} Web 2 answers sorted by: Web the airflow docs say: One for each of the jinja template variables and a templates_dict argument. S3_bucket = variable.get ('bucket_name') print (s3_bucket) example_task () Web obviously, params does not support jinja templating as the sql rendered contains the string literal ' { { task_instance.' rather than the rendered xcom value.
Airflowjinjatemplateexample
{ { conn.test_conn }} so you get any connection attribute like: Adding params to the template_fields in the operator implementation is not enough to force it to render the template. You can use jinja templating with every parameter that is marked as “templated” in the documentation. Additional custom macros can be added globally through plugins, or at a dag level.
Airflowjinjatemplateexample
{ { conn.test_conn }} so you get any connection attribute like: You can use jinja templating with every parameter that is marked as “templated” in the documentation. There is absolutely no problem with doing: Sergiy's is the only way for it to work with your template: Web airflow leverages jinja, a python templating framework, as its templating engine.
Airflowjinjatemplateexample
{ { conn.test_conn }} so you get any connection attribute like: There is absolutely no problem with doing: Assuming you have conn id test_conn you can use macros directly via: For example, say you want to pass the start of the data interval as an environment variable to a bash script using the bashoperator: S3_bucket = variable.get ('bucket_name') print (s3_bucket).
Generating Airflow DAGs using Jinja by Ali Masri Medium
One for each of the jinja template variables and a templates_dict argument. { { conn.test_conn.host }}, { { conn.test_conn.login }}, { { conn.test_conn.password }} and so on. Which variables and functions are available when templating. 2 to add to sergiy's response, it depends on where you want to make your intervention. Web the airflow docs say:
[Airflow] User_defined_macros를 이용하여 jinja template의 사용자 정의 변수 활용하기
Adding params to the template_fields in the operator implementation is not enough to force it to render the template. One for each of the jinja template variables and a templates_dict argument. How to apply jinja templates in your code. Which variables and functions are available when templating. S3_bucket = variable.get ('bucket_name') print (s3_bucket) example_task ()
[Airflow] jinja_template을 활용한 날짜 동적 변수 활용 하는 법(동적 datetime, ds변수 UTC안되는
Sergiy's is the only way for it to work with your template: Web templating airflow passes in an additional set of keyword arguments: You can use jinja templating with every parameter that is marked as “templated” in the documentation. Web the airflow docs say: Which operator fields can be templated and which cannot.
Flask Jinja2 Example Insularmiseria
Web 2 answers sorted by: How to apply jinja templates in your code. My question is does anyone know the requirements to get rendered strings into the ui under the rendered or rendered template tab? Which operator fields can be templated and which cannot. You can use jinja templating with every parameter that is marked as “templated” in the documentation.
The Ultimate FastAPI Tutorial Part 6 Serving HTML with Jinja Templates
Which operator fields can be templated and which cannot. Web templates reference¶ variables, macros and filters can be used in templates (see the jinja templating section) the following come for free out of the box with airflow. One for each of the jinja template variables and a templates_dict argument. Web the airflow docs say: You can use jinja templating with.
GitHub appgenerator/jinjatemplate Jinja Template Free
How to apply jinja templates in your code. Web i've been able to successfully render jinja templates using the function within the baseoperator, render_template. Sergiy's is the only way for it to work with your template: In this guide, you'll learn the following: Web the airflow docs say:
jinja2template · GitHub Topics · GitHub
Web templating airflow passes in an additional set of keyword arguments: It makes sense that specific parameters in the airflow world (such as certain parameters to pythonoperator ) get templated by. Web obviously, params does not support jinja templating as the sql rendered contains the string literal ' { { task_instance.' rather than the rendered xcom value. { { conn.test_conn.
Additional Custom Macros Can Be Added Globally Through Plugins, Or At A Dag Level Through The Dag.user_Defined_Macros Argument.
The templates_dict argument is templated, so each value in the dictionary is evaluated as a jinja template. { { params.etl_date if params.etl_date is not none else execution_date.strftime ('%y%m%d') }} Web airflow leverages jinja, a python templating framework, as its templating engine. Sergiy's is the only way for it to work with your template:
My Question Is Does Anyone Know The Requirements To Get Rendered Strings Into The Ui Under The Rendered Or Rendered Template Tab?
Which operator fields can be templated and which cannot. For example, say you want to pass the start of the data interval as an environment variable to a bash script using the bashoperator: Web 2 answers sorted by: Web templates reference¶ variables, macros and filters can be used in templates (see the jinja templating section) the following come for free out of the box with airflow.
Web Obviously, Params Does Not Support Jinja Templating As The Sql Rendered Contains The String Literal ' { { Task_Instance.' Rather Than The Rendered Xcom Value.
2 to add to sergiy's response, it depends on where you want to make your intervention. Assuming you have conn id test_conn you can use macros directly via: You can use jinja templating with every parameter that is marked as “templated” in the documentation. Web templating airflow passes in an additional set of keyword arguments:
Web 2 Answers Sorted By:
How to apply jinja templates in your code. Adding params to the template_fields in the operator implementation is not enough to force it to render the template. S3_bucket = variable.get ('bucket_name') print (s3_bucket) example_task () Web the airflow docs say:

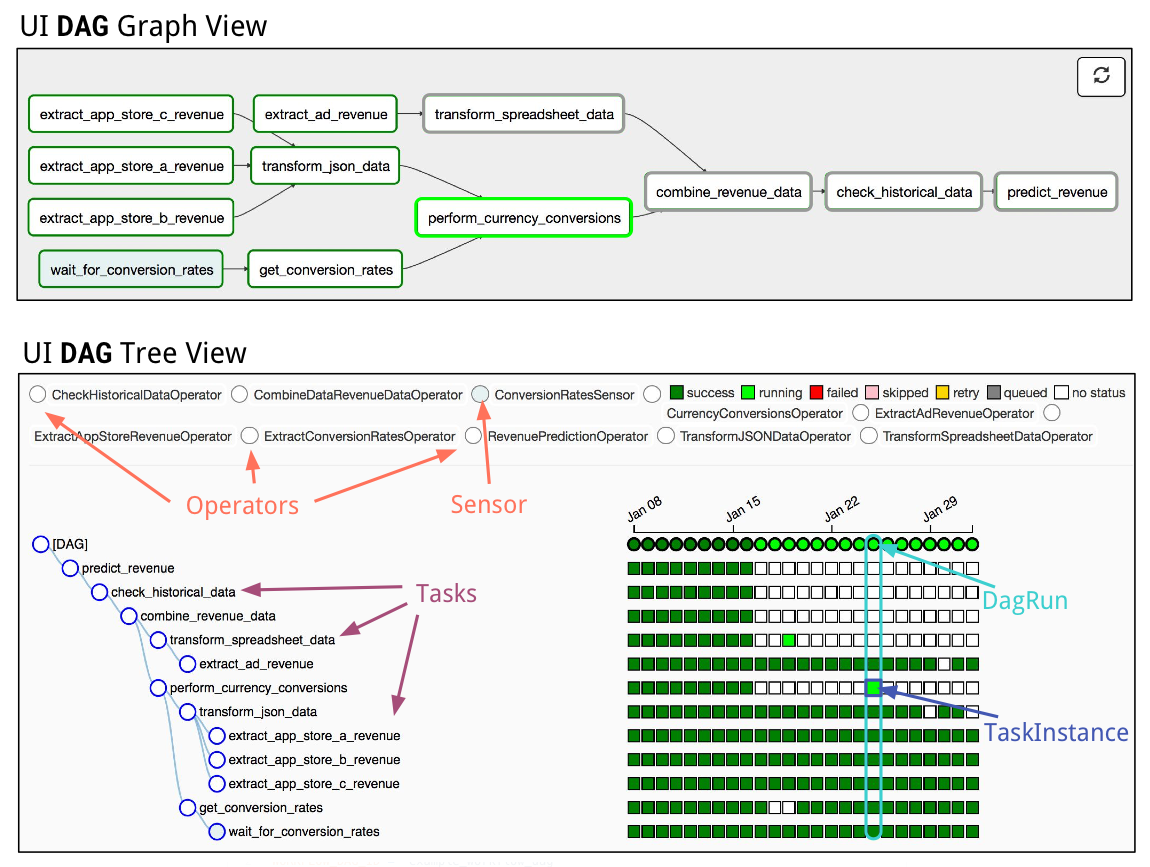

![[Airflow] User_defined_macros를 이용하여 jinja template의 사용자 정의 변수 활용하기](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R1280x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https:%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FqWCcw%2FbtrY2oADnDO%2F4K31UpmQe8bH9LM8xwMfX0%2Fimg.png)
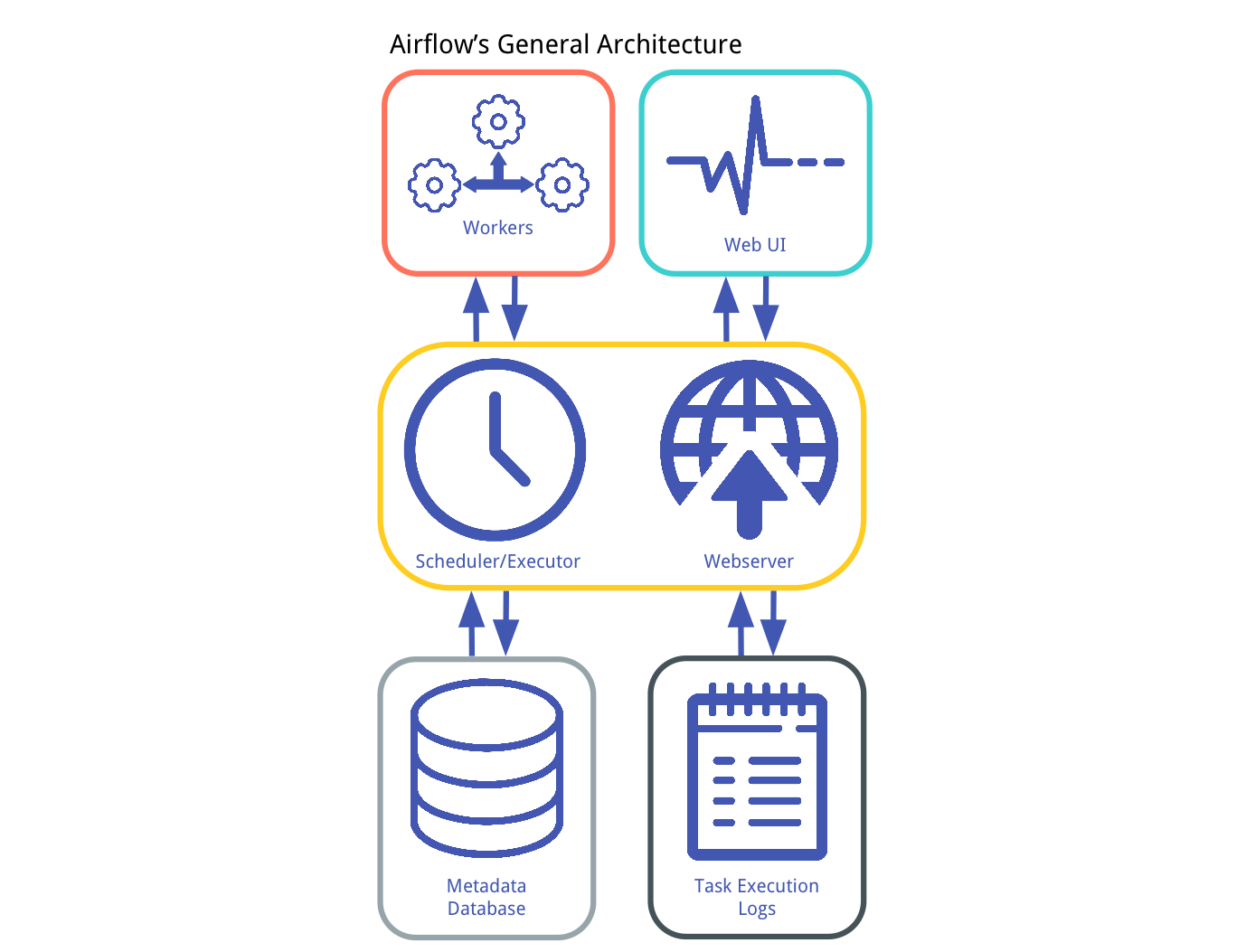
![[Airflow] jinja_template을 활용한 날짜 동적 변수 활용 하는 법(동적 datetime, ds변수 UTC안되는](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R800x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https:%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FcsL9Ic%2FbtrMtGmuu3w%2FnoJRPnQDetPLKE5mLZnQH1%2Fimg.png)